

True polycoria is a very uncommon condition. Each pupil owns an intact sphincter muscle that will become small and dilate.
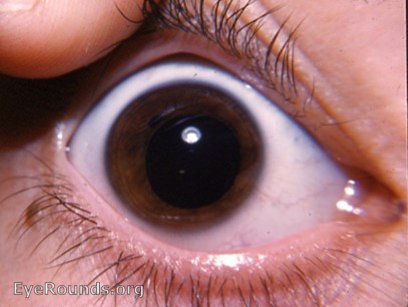
Two additional phenotypes include isolated retinal artery tortuosity and nonsyndromic autosomal dominant congenital cataract. A person with true polycoria has two or more two pupils in one eye. Complete ophthalmic history and eye exam with attention to cornea, tonometry, anterior. HANAC (hereditary angiopathy with nephropathy, aneurysms, and muscle cramps) syndrome usually associates asymptomatic small-vessel brain disease, cerebral large vessel involvement (i.e., aneurysms), and systemic findings involving the kidney, muscle, and small vessels of the eye. Corectopia demonstrating inferiorly displaced pupil. Porencephaly (fluid-filled cavities in the brain detected by CT or MRI) is typically manifest as infantile hemiparesis, seizures, and intellectual disability however, on occasion it can be an incidental finding. Clinically, small-vessel brain disease manifests as infantile hemiparesis, seizures, single or recurrent hemorrhagic stroke, ischemic stroke, and isolated migraine with aura. On imaging studies, small-vessel brain disease is manifest as diffuse periventricular leukoencephalopathy, lacunar infarcts, microhemorrhage, dilated perivascular spaces, and deep intracerebral hemorrhages. The spectrum of COL4A1-related disorders includes: small-vessel brain disease of varying severity including porencephaly, variably associated with eye defects (retinal arterial tortuosity, Axenfeld-Rieger anomaly, cataract) and systemic findings (kidney involvement, muscle cramps, cerebral aneurysms, Raynaud phenomenon, cardiac arrhythmia, and hemolytic anemia).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
